![Seasonal Development and Phenology of Ludwigia peploides: Growth Stages Across the Year[3]](https://ludwigiapeploides.com/img/L6BDmW78wq-UL_IMAGExZfEKS.webp)
2026-01-14
Understanding Ludwigia peploides Growth Patterns
What if a single plant could reshape an entire ecosystem? Understanding the intricate dynamics of Ludwigia peploides, or creeping water primrose, reveals its surprising vitality and impact on biodiversity. As we delve into the seasonal development and ecological significance of this species, the insights gained will empower effective management and restoration efforts in freshwater habitats.
What You Will Learn
- Habitat Preferences: Ludwigia peploides thrives in sunny, nutrient-rich shallow waters, often forming dense mats.
- Ecological Interactions: This plant provides shelter for aquatic organisms but can also disrupt native vegetation.
- Reproductive Strategies: It employs clonal fragmentation and sexual reproduction, affecting its spread and management.
- Impact of Seasonal Changes: Understanding growth timing and hydrological influences is essential for effective control measures.
- Flood Tolerance: Adaptations for survival in dynamic water conditions enhance its resilience and spread.
Seasonal Development and Reproductive Strategies of Ludwigia peploides
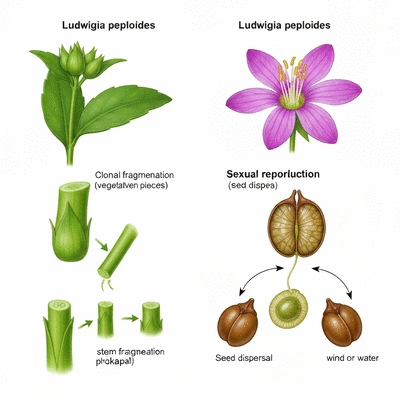
This visual highlights the key aspects of Ludwigia peploides' seasonal development and its dual reproductive strategies: clonal fragmentation and sexual reproduction. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for effective management of this aquatic plant.
Seasonal Development & Growth
-
✓
Growth Timing:
Vigorous stages inform control measures.
-
✓
Habitat Changes:
Water levels/temperature affect growth.
-
✓
Biodiversity Impact:
Influence on native plant communities.
Reproductive Strategies Overview
-
●
Clonal Fragmentation:
Rapid spread via vegetative propagation.
-
●
Sexual Reproduction:
Seed production enhances genetic variability.
-
●
Ecological Implications:
Varied impacts on local ecosystems.
Seed Production & Its Impact
-
■
Dormancy Mechanisms:
Seeds survive in soil for years.
-
■
Germination Triggers:
Moisture and light conditions.
-
■
Impact on Local Flora:
Seedlings outcompete native species.
Hydrological & Pollination Dynamics
-
★
Flood Tolerance:
Adaptations for survival in floods.
-
★
Pollination Agents:
Water currents & insects.
-
★
Dispersal Mechanisms:
Seeds float for long-distance spread.
Understanding the Seasonal Development of Ludwigia peploides
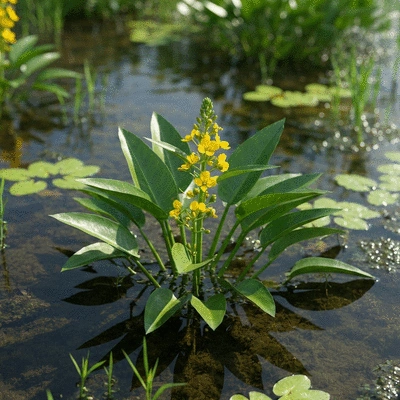
As we dive into the world of Ludwigia peploides, commonly known as creeping water primrose, it's essential to grasp its seasonal development. This aquatic plant exhibits fascinating growth patterns that reflect its adaptability and ecological significance in freshwater ecosystems. By understanding its seasonal cycle, we can better manage its impact on local biodiversity and habitat health.
In this section, we will explore the characteristics of Ludwigia peploides, its habitat preferences, and the ecological interactions it engages in. Knowing these details serves as the foundation for effective management and restoration efforts.
Introduction to Ludwigia peploides: Characteristics and Habitat
Ludwigia peploides is a perennial herb that thrives in shallow waters, often forming dense mats that can outcompete native vegetation. Its vibrant yellow flowers and broad, oval leaves make it a striking presence in wetlands. To fully appreciate its role in aquatic ecosystems, let's examine its habitat preferences and the interactions it has with other species. Research published in the American Journal of Botany provides further insights into the ecology of these invasive aquatic plants.
- Habitat Preferences: Typically found in marshes, lakes, and slow-moving rivers, creeping water primrose prefers areas with abundant sunlight and nutrient-rich waters.
- Ecological Interactions: This plant plays a dual role in its habitat: it provides shelter and food for various aquatic organisms while also potentially disrupting native plant communities.
- Adaptability: Ludwigia peploides can tolerate a range of water levels and temperatures, making it a resilient species in fluctuating environmental conditions.
Understanding these aspects is crucial for land managers and ecologists, as they influence the strategies we employ in controlling this invasive species. Have you noticed its presence in your local waterways? Gathering insights from our community helps shape effective management practices!
Importance of Studying Seasonal Phenology in Aquatic Plants
Studying the seasonal phenology of aquatic plants like Ludwigia peploides is vital for several reasons. First, it helps us understand how these species interact with their environment throughout the year. Second, it provides insights into their growth patterns, which can inform management strategies aimed at preserving native biodiversity. The U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service offers an ecological risk screening summary for floating primrose-willow, highlighting its potential impacts.
- Growth Timing: Understanding when Ludwigia peploides initiates growth can assist in planning control measures during its most vigorous stages.
- Habitat Changes: Seasonal studies reveal how alterations in water levels or temperature affect its growth and reproduction.
- Impact on Biodiversity: By examining its seasonal patterns, we can gauge its influence on surrounding plant communities and aquatic life.

By prioritizing seasonal studies, we can develop a comprehensive approach to managing Ludwigia peploides and restoring ecological balance in impacted habitats.
Pro Tip
To effectively manage Ludwigia peploides, consider timing your control measures to coincide with its growth cycles. Monitoring water levels and seasonal patterns can provide critical insights, allowing for targeted interventions that minimize its spread while promoting the recovery of native plant species.
Reproductive Strategies of Ludwigia peploides
Understanding the reproductive strategies of Ludwigia peploides is essential for effective management of this invasive species. This plant employs two main strategies: clonal fragmentation and sexual reproduction. Each method has its own ecological implications, affecting not only its spread but also the restoration efforts in impacted ecosystems.
Clonal fragmentation allows Ludwigia peploides to rapidly occupy new areas by producing vegetative offspring that can thrive in similar habitats. On the other hand, sexual reproduction generates genetic diversity, which can enhance the plant’s resilience and adaptability. Recognizing these reproductive strategies helps us tailor our management practices effectively.
Clonal Fragmentation vs. Sexual Reproduction: An Overview
When considering the reproductive capabilities of Ludwigia peploides, it's important to examine both clonal fragmentation and sexual reproduction. Clonal fragmentation occurs when parts of the plant break off and establish new roots, leading to rapid population increase. In contrast, sexual reproduction involves the production of seeds, which contributes to genetic diversity.
- Clonal Fragmentation: Quick spread via vegetative propagation.
- Sexual Reproduction: Seed production enhances genetic variability.
- Ecological Implications: Different strategies can lead to varied impacts on local ecosystems.
Both methods are vital for the survival of Ludwigia peploides in fluctuating environments. As we work at the Ludwigia Peploides Resource Center, we encourage ecologists and land managers to pay attention to these reproductive strategies when developing control measures.
Seed Production and Its Ecological Implications
Seed production in Ludwigia peploides plays a significant role in its ability to thrive and invade new territories. The seeds can remain dormant in the soil for extended periods, waiting for favorable conditions to germinate. This resilience is critical in maintaining its population during adverse environmental conditions. Research on the dormancy and germination of Ludwigia seeds, such as that found on PubMed, underscores the complexity of managing its spread.
- Dormancy Mechanisms: Seeds can survive in soil for years.
- Germination Triggers: Ideal moisture and light conditions.
- Impact on Local Flora: Seedlings can outcompete native species quickly.
Understanding these dynamics sheds light on how Ludwigia peploides can overwhelm ecosystems. As someone dedicated to fostering ecological balance, I see the need for informed management strategies that consider these reproductive characteristics.
Impact of Hydrological Regimes on Reproductive Timing
The timing of reproduction in Ludwigia peploides is closely linked to hydrological regimes. Changes in water levels can influence both flowering periods and seed production, impacting the plant's success in colonizing new areas. Being aware of these interactions helps us predict and manage its spread more effectively.
For instance, during periods of flooding, the plant may focus on producing seeds that are adapted to disperse via water, while in drier conditions, it may rely more on vegetative reproduction. Understanding these patterns is essential for developing effective management plans.
Flood Tolerance Traits and Their Role in Survival
Flood tolerance is a crucial trait for Ludwigia peploides, enabling it to survive and reproduce in dynamic freshwater ecosystems. The ability to endure prolonged submersion or rapid changes in water levels allows this plant to thrive where many others cannot.
- Adaptations: Specialized structures for gas exchange.
- Survival Mechanisms: Rapid resprouting after flooding.
- Implications for Management: Requires targeted strategies to mitigate its spread.
As part of our mission at the Ludwigia Peploides Resource Center, we strive to share insights on these adaptations, ensuring that land managers and ecologists are equipped to handle this resilient species.
Pollination and Seed Dispersal Dynamics in Freshwater Habitats
Pollination is another critical aspect of Ludwigia peploides reproductive success. The plant typically relies on water and insects for pollination, which can vary with environmental conditions. Understanding these dynamics allows us to assess the potential for seed dispersal and population establishment in new areas.
- Pollination Agents: Water currents and pollinators like bees and other insects.
- Dispersal Mechanisms: Seeds can float, allowing for long-distance spread.
- Management Considerations: Timing of control measures to coincide with flowering and seed set.
By studying these reproductive dynamics, we can develop more effective strategies for managing Ludwigia peploides and restoring ecological balance in affected habitats.
Frequently Asked Questions about Ludwigia peploides
- What is Ludwigia peploides?
Ludwigia peploides, also known as creeping water primrose, is a perennial aquatic plant that can significantly impact freshwater ecosystems.
- Where does Ludwigia peploides typically grow?
It thrives in shallow, sunny, nutrient-rich waters such as marshes, lakes, and slow-moving rivers, often forming dense mats.
- How does Ludwigia peploides reproduce?
It uses two main strategies: clonal fragmentation (rapid spread via vegetative parts) and sexual reproduction (seed production for genetic diversity and long-term survival).
- What are the ecological impacts of Ludwigia peploides?
While it provides shelter for some aquatic organisms, it can also outcompete native vegetation, disrupt natural habitats, and alter biodiversity.
- Why is understanding its seasonal development important for management?
Knowing its growth timing and how it responds to seasonal changes (like water levels and temperature) helps in planning effective control measures during its most vulnerable or vigorous stages.
- Can Ludwigia peploides survive floods?
Yes, it has significant flood tolerance traits, including specialized structures for gas exchange and rapid resprouting, which enable it to survive and reproduce in dynamic water conditions.
- How are its seeds dispersed?
Seeds can remain dormant in soil for years and are often dispersed by water currents, allowing for long-distance spread, and germination is triggered by moisture and light.
Recap of Key Points
Here is a quick recap of the important points discussed in the article:
- Characteristics and Habitat: Ludwigia peploides thrives in shallow, nutrient-rich waters, often forming dense mats that outcompete native vegetation.
- Seasonal Phenology: Understanding its seasonal growth patterns is crucial for developing effective management strategies to preserve biodiversity.
- Reproductive Strategies: The plant employs clonal fragmentation for rapid spread and sexual reproduction for genetic diversity, both of which influence its management.
- Flood Tolerance: Flood tolerance traits enable Ludwigia peploides to survive in dynamic environments, necessitating targeted management approaches.
- Pollination Dynamics: Water and insects serve as pollinators, with seed dispersal mechanisms contributing to its invasive potential.
![Seasonal Development and Phenology of Ludwigia peploides: Growth Stages Across the Year[3]](https://ludwigiapeploides.com/img/L6BDmW78wq-UL_IMAGExZfEKS.webp)


![Comparative Biology: Ludwigia peploides vs. Ludwigia hexapetala – Key Differences and Identification Tips[2]](https://ludwigiapeploides.com/img/ALX99HCoPd-UL_IMAGERH26Sp-t.webp)


![Seasonal Development and Phenology of Ludwigia peploides: Growth Stages Across the Year[3]](https://ludwigiapeploides.com/img/L6BDmW78wq-UL_IMAGExZfEKS-t.webp)
Ludwigia Species Identification Guide
Monitoring Ludwigia peploides Recovery Efforts
Ludwigia Peploides: A Regional Study
Understanding Ludwigia peploides Growth Patterns
IPM Strategies for Ludwigia Control