
Monitoring Ludwigia peploides Recovery Efforts
Engaging in the management of invasive species requires a commitment to understanding their long-term impact on ecosystems. What if you could not only remove an invasive plant but also ensure the health of the entire habitat? This article dives deep into the vital role of long-term monitoring in eradicating Ludwigia peploides.
What You Will Learn
- The critical importance of post-eradication monitoring for assessing ecosystem health.
- Key goals of long-term monitoring, including evaluating regrowth and control strategies.
- Integration of biodiversity assessments into monitoring practices to enhance ecosystem resilience.
- Essential monitoring techniques such as vegetation transects and water quality analysis for effective management.
- Strategies for engaging community stakeholders in the monitoring process to foster collaborative management efforts.
Ludwigia Peploides Monitoring: Key Protocols and Goals
This visual outlines the crucial processes and objectives for effective long-term monitoring in Ludwigia peploides eradication efforts, ensuring ecological recovery and preventing resurgence.
Key Goals of Long-Term Monitoring
- ✓ Assessing regrowth of Ludwigia peploides
- ✓ Evaluating effectiveness of control strategies
- ✓ Measuring ecosystem restoration (flora & fauna)
- ✓ Detecting potential threats to biodiversity
Essential Monitoring Protocols
- Pre-Treatment Assessment: Establish baseline via vegetation transects and water quality. (e.g., dissolved oxygen, pH)
- Post-Treatment Techniques:
- Vegetation Transects (for regrowth & density)
- Water Quality Analysis (ecosystem health)
- Regrowth Checks (roots & fragments)
- Field Surveys (comprehensive data)
Adaptive Management Cycle
1. Review Data
Identify trends in monitoring data.
2. Adjust Strategies
Refine eradication efforts based on findings.
3. Engage Stakeholders
Involve community in adaptive process.
Understanding Long-Term Monitoring Protocols for Ludwigia peploides Eradication
As we delve into the realm of invasive species management, understanding the significance of long-term monitoring protocols for Ludwigia peploides eradication is pivotal. This process isn't just about removing a plant—it's about ensuring the health of the entire ecosystem. Effective monitoring post-eradication helps us gauge the success of our efforts and maintain ecological balance.
Monitoring after we take steps to eradicate Ludwigia peploides is crucial. It allows us to observe any resurgence of this plant and assess how our interventions impact the surrounding environment. By keeping a close eye on the ecosystem, we can prevent future invasions and promote a thriving habitat for native species. For more details on aquatic invasive species control projects, you can refer to resources from the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation.
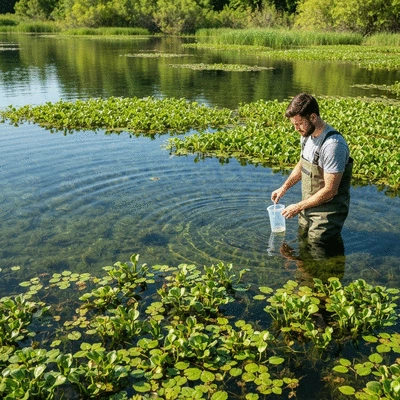

The Importance of Post-Eradication Monitoring
Why is monitoring so vital after the eradication of creeping water primrose? The answer lies in our commitment to ecological health. Post-eradication monitoring provides critical data that helps us understand the effectiveness of our strategies and the overall health of the aquatic ecosystem.
- Detecting regrowth of Ludwigia peploides
- Assessing the recovery of native flora and fauna
- Evaluating the impact of management strategies
- Measuring the overall restoration of the ecosystem
By focusing on these areas, we can develop more effective management plans and engage stakeholders in meaningful ways. This ongoing vigilance ensures that we preserve the ecological integrity of our waterways. A comprehensive management plan for Ludwigia peploides can be found by consulting documents such as the Peconic River Management Plan.
Key Goals of Long-Term Monitoring
When we talk about long-term monitoring, it's essential to have clear objectives in mind. The primary goals include assessing regrowth of Ludwigia peploides, evaluating the effectiveness of control strategies, and measuring ecosystem restoration. These objectives guide us in refining our techniques and adapting to new challenges.
- Assessing regrowth: Monitoring how quickly Ludwigia peploides returns to treated areas is vital for understanding our control methods.
- Evaluating control strategies: We need to analyze which methods work best in different environments.
- Measuring ecosystem restoration: Are our local ecosystems bouncing back? Monitoring flora and fauna recovery provides insight.
These goals not only help us track our progress but also empower land managers and ecologists to make informed decisions moving forward. To foster collaboration, sharing our findings with local communities is essential.
Integrating Biodiversity into Monitoring Practices
Long-term monitoring isn't just about managing Ludwigia peploides—it's also about supporting the recovery of native species and enhancing overall biodiversity within the ecosystem. By incorporating biodiversity assessments into our monitoring protocols, we can gain a deeper understanding of how invasive species impact local flora and fauna.
- Tracking native species recovery
- Assessing habitat quality and health
- Identifying potential threats to biodiversity
- Engaging community members in biodiversity initiatives
Focusing on biodiversity allows us to create a more resilient ecosystem, ultimately benefiting both human and wildlife populations. By collaborating with local stakeholders, such as community organizations, we can develop strategies that promote ecological balance.
Frequently Asked Questions about Ludwigia Peploides Monitoring
What is the primary purpose of long-term monitoring for Ludwigia peploides eradication?
The primary purpose is to assess the success of eradication efforts, prevent resurgence of the invasive plant, and ensure the overall health and recovery of the affected ecosystem.
What are the key goals of long-term monitoring?
Key goals include assessing regrowth of Ludwigia peploides, evaluating the effectiveness of control strategies, measuring ecosystem restoration (flora and fauna), and detecting potential threats to biodiversity.
Why is biodiversity assessment important in monitoring practices?
Integrating biodiversity assessments helps track the recovery of native species, assess habitat quality, identify threats to biodiversity, and create a more resilient ecosystem following invasive species removal.
What monitoring techniques are essential for effective management?
Essential techniques include pre-treatment assessments to establish baselines, post-treatment vegetation transects, water quality analysis, regular regrowth checks for roots and fragments, and comprehensive field surveys for data collection.
How can community members be involved in the monitoring process?
Community members can be engaged through workshops, volunteer monitoring programs, and educational resources. This fosters a sense of ownership and provides additional support for monitoring activities and awareness.
Essential Monitoring Protocols for Effective Management
Implementing essential monitoring protocols is critical for effective management of Ludwigia peploides. These protocols provide a structured approach to assess the effectiveness of eradication efforts and ensure long-term success. Further information on this invasive plant, often known as floating water primrose, can be found through organizations like LIISMA (Long Island Invasive Species Management Area).
Pre-Treatment Assessment: Setting a Baseline
Before we begin the eradication process, conducting a thorough pre-treatment assessment is key. This involves establishing a baseline through vegetation transects and water quality analyses. By documenting the initial conditions, we can measure changes over time and assess the impact of our management strategies.
Post-Treatment Monitoring Techniques
Once we've implemented eradication strategies, it's crucial to monitor the effects through various techniques. Here are some effective methods:
Vegetation Transects
Vegetation transects are a powerful tool for tracking regrowth of Ludwigia peploides and assessing the efficacy of our control methods. By systematically measuring vegetation density and diversity along set transects, we can identify changes in the plant community.
Water Quality Analysis
Monitoring water quality is also essential to our success. Key metrics such as dissolved oxygen levels, pH, and nutrient concentrations provide insight into the health of the ecosystem and indicate whether conditions are favorable for native species recovery.

Regrowth Checks: Monitoring Roots and Fragments
After eradication, we must be vigilant about potential regrowth from roots and fragments. Employing regular regrowth checks ensures that we catch any resurgence early and can take action before it spreads further into the ecosystem.
Field Surveys for Effective Data Collection
Finally, conducting field surveys is vital for gathering comprehensive data to inform our monitoring protocols. These surveys allow us to assess the ecological impacts of our management efforts and adjust our strategies accordingly.
Adaptive Management Strategies for Ongoing Success
Adaptive management plans are crucial for ongoing success. By incorporating annual reviews and adjustments based on monitoring data, we can refine our approaches to Ludwigia peploides management.
- Regularly review monitoring data to identify trends
- Adjust eradication strategies based on findings
- Engage stakeholders in the adaptive management process
This iterative process allows us to respond effectively to changing conditions and improve our efforts towards sustainable ecosystem restoration. Together, we can ensure that our waterways remain healthy and vibrant.
Pro Tip
To enhance the effectiveness of your long-term monitoring efforts, consider implementing community-driven initiatives. Engaging local volunteers not only fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility but also provides additional manpower for regular monitoring activities. This collaborative approach can significantly amplify your data collection efforts and promote awareness of the importance of managing Ludwigia peploides within your ecosystem.
Summarizing the Importance of Long-Term Monitoring
Long-term monitoring after Ludwigia peploides eradication is vital for ensuring the health of our ecosystems. It allows us to assess whether our efforts have been successful and to understand the long-term effects of invasive species management. By keeping a close eye on the ecology of the area, we can better protect native habitats and restore balance.
A few key takeaways about the significance of long-term monitoring include:
- Assessment of Regrowth: Monitoring helps us quickly identify any regrowth of Ludwigia peploides, allowing timely interventions.
- Evaluation of Control Strategies: We can measure the effectiveness of different management methods and adapt our approaches accordingly.
- Biodiversity Support: Long-term monitoring aids in tracking the recovery of native species, contributing to overall ecosystem health.
In essence, continuous observation and assessment provide the information necessary to maintain the success of our eradication efforts and ensure that the ecological balance is restored over time.
Engaging Stakeholders in the Monitoring Process
Engaging community members and stakeholders in the monitoring process is essential for the success of invasive species management. Collaborative efforts can enhance the effectiveness of our monitoring initiatives and foster a shared commitment to ecosystem health. By building a network of involved stakeholders, we can create a more resilient approach to managing Ludwigia peploides.
Community Engagement and Educational Outreach
Involving local communities in monitoring efforts not only raises awareness but also empowers individuals to take action. Here are some strategies for fostering community engagement:
- Workshops and Training: Organizing hands-on workshops to educate community members about Ludwigia peploides and effective monitoring techniques.
- Volunteer Monitoring Programs: Establishing programs that allow community members to participate in field surveys and monitoring activities.
- Educational Resources: Providing accessible materials, such as identification guides and management strategies, to enhance understanding.
By cultivating a sense of ownership in the monitoring process, we can inspire communities to actively engage in preserving their local ecosystems.
Next Steps for Effective Monitoring Implementation
As we move forward with our initiatives, it's crucial for all involved to adopt recommended monitoring practices. By doing so, we can ensure that our efforts to manage Ludwigia peploides are grounded in evidence and tailored for success. I encourage you to connect with local environmental organizations to learn more about how you can participate in this vital work. Together, we can create a healthier environment for future generations!
Stay Informed and Get Involved
To stay updated on best practices, new research, and ongoing projects related to Ludwigia peploides monitoring, I invite you to subscribe to our newsletter. Our team at the Ludwigia Peploides Resource Center is committed to sharing valuable insights and resources that can help empower your efforts in managing invasive species. Let’s work together to protect our ecosystems and foster biodiversity!
Recap of Key Points
Here is a quick recap of the important points discussed in the article:
- Importance of Post-Eradication Monitoring: Essential for assessing the regrowth of Ludwigia peploides and understanding the ecological health of affected areas.
- Key Goals of Monitoring: Focus on assessing regrowth, evaluating control strategies, and measuring ecosystem restoration to adapt management plans effectively.
- Integrating Biodiversity Assessments: Supports the recovery of native species and enhances overall ecosystem resilience by tracking habitat quality and potential threats.
- Essential Monitoring Protocols: Include pre-treatment assessments, regular regrowth checks, and thorough field surveys to gather comprehensive data.
- Adaptive Management Strategies: Regular reviews of monitoring data allow for adjustments in eradication strategies based on findings and stakeholder engagement.
![Comparative Biology: Ludwigia peploides vs. Ludwigia hexapetala – Key Differences and Identification Tips[2]](https://ludwigiapeploides.com/img/ALX99HCoPd-UL_IMAGERH26Sp-t.webp)


![Seasonal Development and Phenology of Ludwigia peploides: Growth Stages Across the Year[3]](https://ludwigiapeploides.com/img/L6BDmW78wq-UL_IMAGExZfEKS-t.webp)
Ludwigia Species Identification Guide
Monitoring Ludwigia peploides Recovery Efforts
Ludwigia Peploides: A Regional Study
Understanding Ludwigia peploides Growth Patterns
IPM Strategies for Ludwigia Control