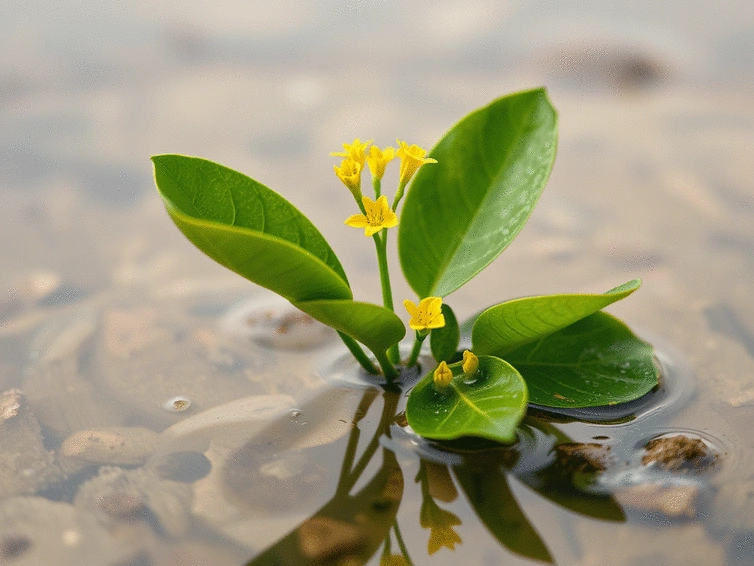

Ludwigia Peploides: Impact on Habitat
Did you know that a single plant species can redefine entire aquatic ecosystems? Ludwigia peploides, or creeping water primrose, serves as a remarkable example of both beauty and ecological complexity. Its presence in water bodies illustrates a delicate balance between providing habitat and posing threats to biodiversity.
What You Will Learn
- Ludwigia peploides thrives in shallow freshwater habitats, forming extensive mat-like structures that can cover large areas.
- This plant exhibits invasive characteristics, reproducing both sexually and vegetatively, allowing rapid spread and competition with native flora.
- While it can enhance aquatic habitats by providing shelter and improving water quality, it also risks displacing native species and disrupting food webs.
- Dense mats of Ludwigia influence sedimentation rates and water flow, potentially leading to ecological consequences such as oxygen depletion and altered nutrient cycling.
Ecological Dynamics of Ludwigia Peploides
This visual summarizes the dual ecological impacts and key characteristics of Ludwigia Peploides, highlighting its invasive traits versus its potential benefits and how it influences sedimentation and water quality.
Understanding the Ecological Role of Ludwigia Peploides
To grasp the ecological role of Ludwigia peploides, we need to delve into the unique characteristics of this remarkable plant. Commonly referred to as the creeping water primrose, Ludwigia peploides is a perennial aquatic herb found in shallow freshwater habitats. Its vibrant yellow flowers and distinct floating leaves make it easily identifiable, but there's much more beneath the surface.
As an ecologist, I've dedicated much of my research to understanding not just the beauty of Ludwigia peploides but also the complexities of its interactions within ecosystems. This plant plays a significant role in shaping the environments it inhabits, which brings both advantages and challenges.
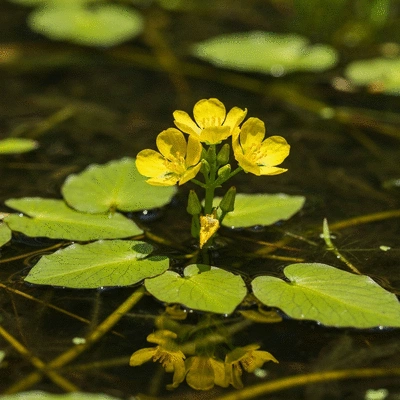

Overview of Ludwigia Peploides: The Water Primrose
Ludwigia peploides thrives in a variety of water bodies, including lakes, ponds, and marshes. Here are some essential characteristics that define this species:
- Growth Form: It develops extensive mat-like structures that can cover large areas of water.
- Flowering: The plant produces striking yellow flowers during the warm months, attracting pollinators.
- Habitat Preferences: Prefers shallow waters with slow-moving or stagnant conditions, allowing it to establish dense populations.
These traits allow Ludwigia peploides to outcompete many native plants, which can lead to significant ecological shifts in its habitat.
Invasive Characteristics and Adaptations
The invasive nature of Ludwigia peploides stems from its remarkable adaptations. This species doesn't just grow; it thrives under conditions that would challenge many other plants. For example, its ability to reproduce both sexually and vegetatively enables rapid spread, often overwhelming native flora.
Additionally, its flexible growth habits and nutrient uptake efficiency make it exceptionally resilient. This adaptability allows Ludwigia peploides to persist in various environments, including those impacted by human activity.
Significance of Ludwigia Peploides in Aquatic Ecosystems
Ludwigia peploides serves dual roles in aquatic ecosystems—while it can provide beneficial habitats for some organisms, it also poses threats to biodiversity. Here are some key points regarding its ecological significance:
- Habitat Creation: Dense mats of Ludwigia can offer shelter for small aquatic organisms and breeding sites for fish.
- Nutrient Cycling: By absorbing excess nutrients, this plant can help improve water quality in eutrophic conditions.
- Altered Food Webs: However, its dominance can lead to the displacement of native species, disrupting existing food webs.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for effective management and restoration efforts, which is a focal point of our mission at the Ludwigia Peploides Resource Center.
Interactive Poll: Your Experience with Ludwigia Peploides
Have you encountered Ludwigia peploides in your local waterways? We want to hear about your experiences! Share your thoughts below:
Impacts of Ludwigia Peploides on Sedimentation
The ecological impact of Ludwigia peploides is profound, especially regarding sedimentation in aquatic environments. Understanding how its dense mats influence water flow and sedimentation rates can help us manage its presence more effectively. Let’s explore the mechanisms at work and their ecological consequences.
How Dense Mats Affect Water Flow and Sedimentation Rates
Ludwigia peploides forms thick mats that float on the water's surface, significantly altering the physical characteristics of the habitat. These dense growth formations can reduce water flow, leading to a buildup of sediments beneath them. Here are some key effects:
- Reduced water circulation: This can lead to stagnant areas where sediments accumulate.
- Increased sedimentation rates: The mats trap particles that would otherwise remain suspended in the water.
- Altered sediment composition: Changes in the types of sediments that settle can impact the overall aquatic ecosystem.
As we consider these impacts, it’s crucial to recognize the potential for long-term changes to water quality and habitat structure.
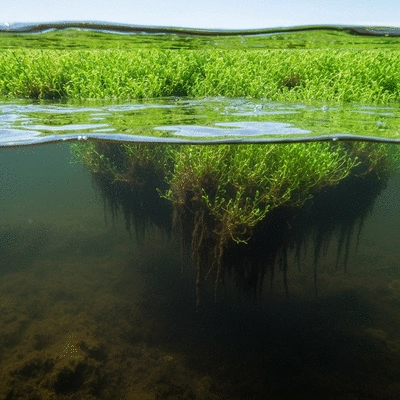

Mechanisms of Particle Trapping and Their Ecological Consequences
Understanding how Ludwigia peploides traps particles is vital. The plant’s leaves and stems create a barrier that slows water movement, allowing sediments to settle. This process can lead to significant ecological consequences, including:
- Loss of nutrient balance: An excess of sediment can cause nutrient overloads, affecting water quality.
- Impacts on aquatic life: Many organisms rely on clear water for survival; increased sedimentation can suffocate fish eggs and disrupt breeding.
- Changes in habitat structure: Over time, altered sedimentation can reshape the landscape, affecting how organisms interact with their environment.
By understanding these mechanisms, we can better appreciate the complexity of ecosystem dynamics influenced by invasive species like Ludwigia peploides.
The Relationship Between Sedimentation and Oxygen Levels
As sediment accumulates due to the presence of Ludwigia peploides, the relationship between sedimentation and oxygen levels becomes increasingly important. High sedimentation often leads to oxygen depletion, creating conditions unfavorable for many aquatic organisms.
Understanding Dystrophic Crises: Nutrient Shifts and Allelopathy
Dystrophic crises occur when excessive nutrients lead to an algal bloom, ultimately resulting in low oxygen levels or hypoxia. Ludwigia peploides contributes to these crises through nutrient cycling and allelopathic interactions. The plant releases chemicals that can suppress the growth of other native flora, further disrupting the balance of the ecosystem, as detailed in a study on allelopathic effects in aquatic plants.
The Role of Ludwigia Peploides in Sediment Retention and Water Quality
Despite its negative impacts, Ludwigia peploides can also play a role in sediment retention, albeit in a harmful context. While it traps sediment, it can also lead to poor water quality due to the buildup of organic matter and the subsequent decay process. This duality highlights the complexity of managing aquatic ecosystems where this species is prevalent.
Frequently Asked Questions about Ludwigia Peploides
What is Ludwigia Peploides?
Ludwigia peploides, also known as creeping water primrose, is a perennial aquatic herb that thrives in shallow freshwater habitats. It is characterized by its vibrant yellow flowers and floating leaves and is known for forming extensive mat-like structures.
Why is Ludwigia Peploides considered invasive?
It is considered invasive due to its remarkable ability to reproduce both sexually and vegetatively, allowing for rapid spread. Its flexible growth habits and efficient nutrient uptake enable it to outcompete many native plant species, leading to ecological disruptions.
What are the dual roles of Ludwigia Peploides in aquatic ecosystems?
While dense mats of Ludwigia can provide shelter for small aquatic organisms and absorb excess nutrients to improve water quality, its dominance can also displace native species, disrupt food webs, and alter sedimentation rates, negatively impacting overall biodiversity.
How does Ludwigia Peploides affect sedimentation and water flow?
Its dense mats significantly reduce water circulation, leading to stagnant areas where sediments accumulate. This increases sedimentation rates and alters sediment composition, which can result in long-term changes to water quality and habitat structure, including oxygen depletion.
What are dystrophic crises and how does Ludwigia Peploides contribute to them?
Dystrophic crises are caused by excessive nutrients leading to algal blooms and subsequent low oxygen levels (hypoxia). Ludwigia peploides contributes by influencing nutrient cycling and releasing allelopathic chemicals that suppress native flora, exacerbating these crises and leading to poor water quality from organic decay.
Recap of Key Points
Here is a quick recap of the important points discussed in the article:
- Ludwigia peploides, or creeping water primrose, thrives in shallow freshwater habitats and is easily identifiable by its yellow flowers and floating leaves.
- The plant's invasive nature is attributed to its ability to reproduce both sexually and vegetatively, enabling rapid spread and displacement of native species.
- While it creates habitats for some aquatic organisms, Ludwigia peploides can also disrupt food webs and alter sedimentation rates, impacting overall water quality.
- Its dense mats can reduce water circulation, leading to sediment accumulation and changes in habitat structure that may negatively affect aquatic life.
- Understanding the ecological implications of Ludwigia peploides is crucial for effective management and restoration of impacted ecosystems.




Monitoring Ludwigia Peploides Spread Strategies
Ludwigia peploides: Water and Stress
Disposing of Ludwigia Peploides Safely
Ecological Risks of Ludwigia Peploides
Ludwigia Species Identification Guide